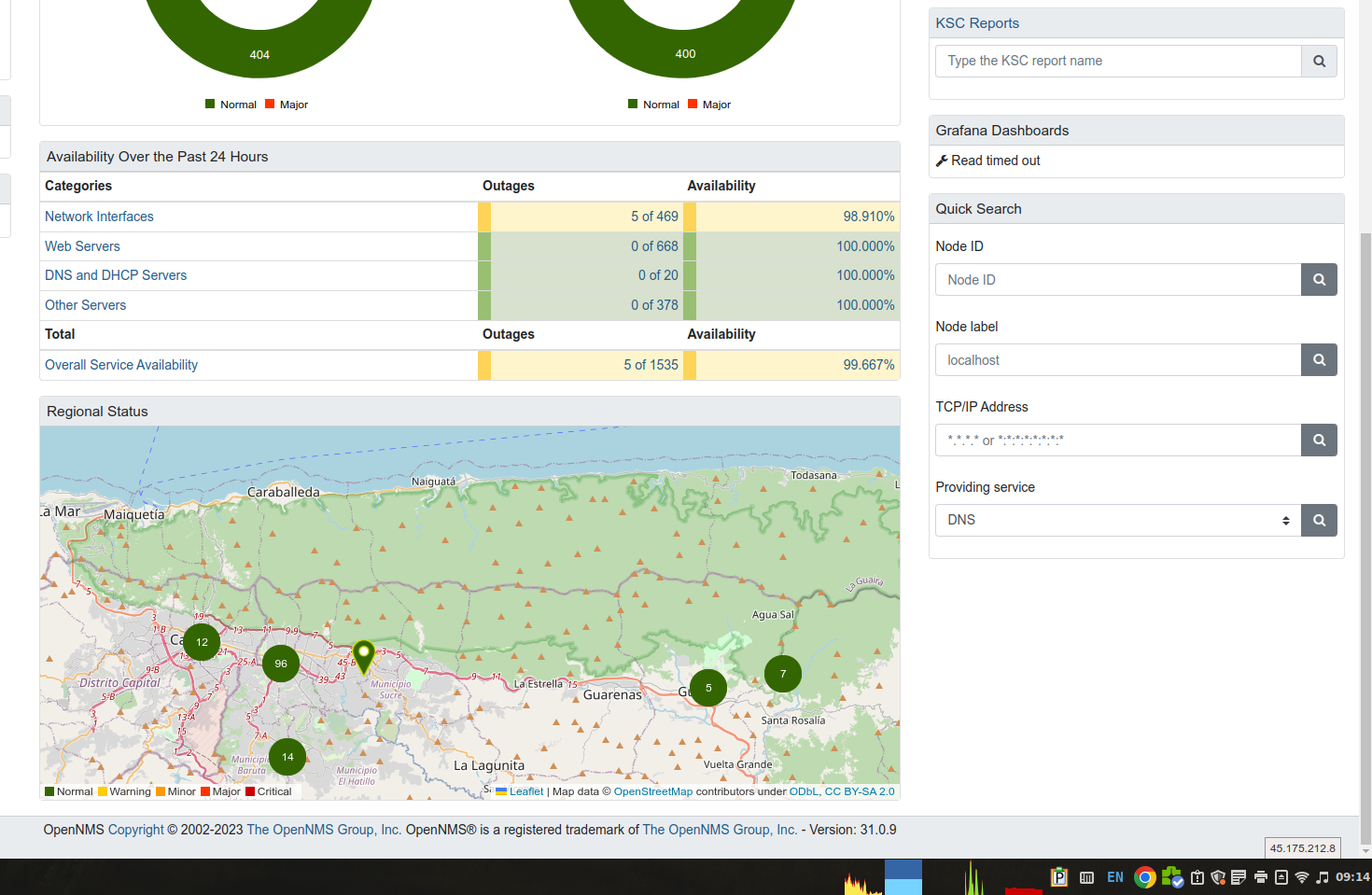
In today's hyper-connected world, where billions of users interact with websites, applications, and services every second, network monitoring solutions are critical to ensuring your network operations stay consistent and reliable. When deployed effectively, they provide continuous surveillance of your network traffic, performance, and security, allowing your team to proactively identify potential trouble spots and address issues, from slow loading times to security threats, before they disrupt services.
With the right network monitoring solution in place, you can not only enhance the performance and security of your networks but also deliver a reliable and seamless internet experience for your users.
What are Network Monitoring Solutions?
Network monitoring solutions give administrators real-time visibility into network activity, enabling them to detect and respond to anomalies promptly. By monitoring for unusual patterns or suspicious activity, network monitoring solutions can help prevent cyber-attacks such as malware infections, DDoS attacks, and data breaches, which can cripple an organization's online presence and reputation.
Network monitoring solutions can also help you optimize network performance by targeting and mitigating bottlenecks and congestion points. Network administrators can ensure that resources are allocated efficiently, preventing slowdowns and traffic blockages that can impede user experience.
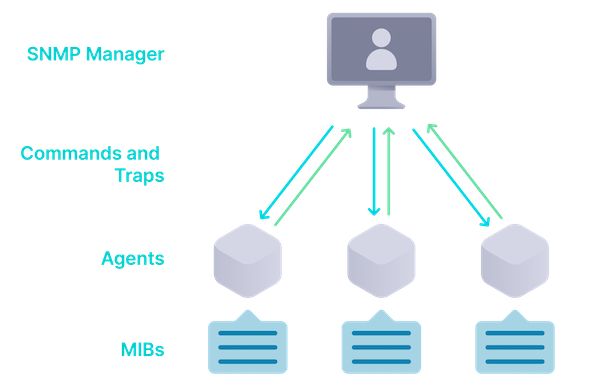
“Distributed environments require a network monitoring solution that is deployable in a dispersed configuration to reach into systems and networks that would otherwise be inaccessible while keeping the monitoring logic centralized for easier operation and administration.
Network Monitoring FAQ
Why is network monitoring important?
Network monitoring is important because it helps ensure the smooth operation of networks by identifying and mitigating issues before they escalate. It also helps optimize network performance, detect security threats, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
How does a network monitoring solution work?
A network monitoring solution works by collecting data from network devices and traffic, analyzing this data to identify issues and trends, and presenting the findings to administrators through reports, alerts, and visualizations.
What are the benefits of using a network monitoring solution?
The benefits of using a network monitoring solution include improved network performance and reliability, enhanced security, reduced downtime, and increased operational efficiency.
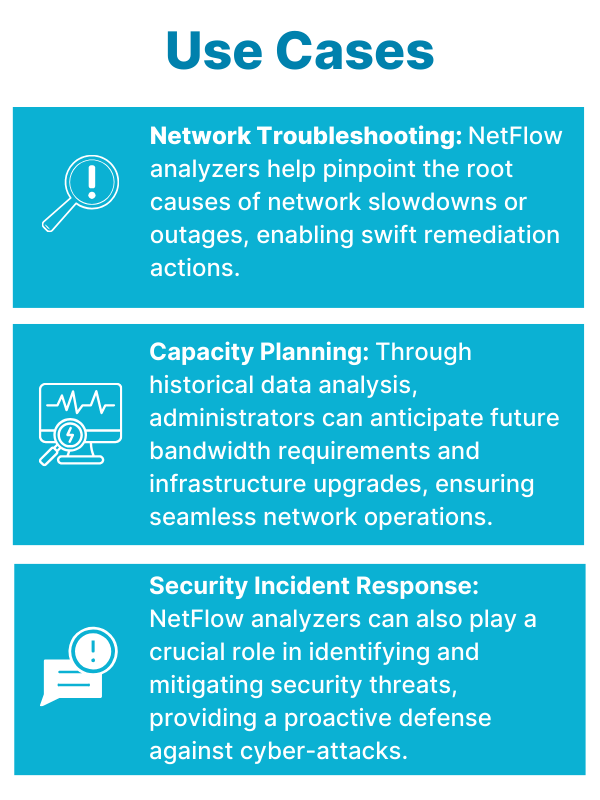
How do network monitoring solutions help with troubleshooting?
Network monitoring solutions help troubleshoot by providing real-time visibility into network performance and security, allowing administrators to quickly identify and resolve issues.
How can I choose the right network monitoring solution for my organization?
When choosing a network monitoring solution, consider the scale and complexity of your network, your budget, the features, ease of use and integration capabilities of the solution, and the level of support the vendor provides. It's also a good idea to try out a few different solutions before deciding.

Network Monitoring Solutions Features
Network monitoring solutions should include various features to empower network administrators to monitor and maintain their networks more efficiently.
Network Traffic Monitoring: Track the flow of data within a network, capturing information about the volume, sources, and destinations of traffic. This helps identify normal behavior patterns and anomalies that may indicate network issues or security threats. Administrators can detect and resolve issues such as bandwidth congestion, network bottlenecks, and unauthorized access attempts.
Performance Monitoring: Performance monitoring involves tracking the performance of network devices, servers, and applications to confirm they are operating efficiently. This includes monitoring metrics such as response times, packet loss, and resource utilization. This helps identify and address issues that can impact user experience, such as slow application performance, network latency, and server downtime. Administrators can optimize network resources, improve reliability, and enhance overall user satisfaction.
Security Monitoring: Security monitoring involves detecting and responding to security threats within the network. This includes monitoring for malware infections, unauthorized access attempts, and data breaches. Techniques include intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and log analysis to identify and mitigate security threats. Administrators are empowered to protect sensitive data, maintain regulatory compliance, and prevent costly security breaches.
Alerting and Reporting: Alerting and reporting features notify administrators of critical events or issues within the network and provide detailed reports on network performance and security. Alerts can notify administrators via email, SMS, or other means when predefined thresholds are exceeded, or anomalies are detected. Reports provide valuable insights into network performance trends, security incidents, and service level agreements (SLAs) compliance. Timely alerts and reports enable administrators to respond quickly to issues, track network performance, and make informed network management and optimization decisions.
Configuration Management: Configuration management features help ensure network devices are optimized for performance and security. This includes managing device configurations, applying configuration changes, and auditing configurations for compliance with best practices and security policies. Configuration management helps reduce the risk of misconfigurations that can lead to network downtime, security vulnerabilities, and performance issues.
Scalability and Flexibility: Network monitoring solutions should accommodate the size and complexity of your network. This includes the ability to monitor a large number of devices and network segments, as well as the ability to integrate with other systems and tools. Administrators can adapt the monitoring environment to meet changing network requirements and integrate with existing network infrastructure and management tools. Monitoring capabilities should grow with the network and meet its evolving needs.
Data Sources for Network Monitoring
Network monitoring solutions must collect and process tens of thousands of data points per second from a variety of network devices. And networks are not static: the volume of data to be processed increases as your network expands. This changes with fluctuations in network traffic, peak hours, and other factors. Network monitoring solutions that can scale dynamically to collect and process large volumes of data help administrators respond to the most current issues promptly.
These are just some example data sources:
Traffic Data: Network traffic, including the volume of traffic, the types of traffic (e.g., web traffic, email traffic), and the sources and destinations of traffic, lets administrators monitor network performance, detect anomalies, and identify potential security threats.
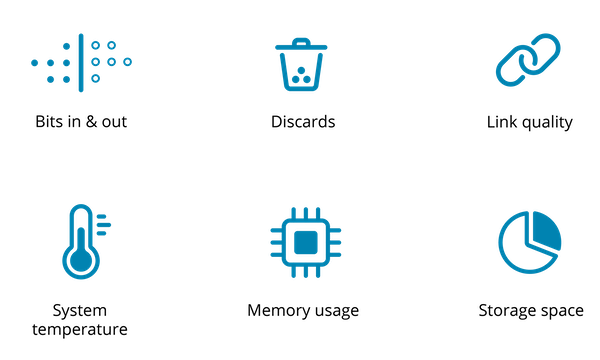
Performance Metrics: Performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory usage, disk I/O, and network bandwidth from network devices, including routers, switches, and servers, so administrators can monitor the health and performance of network devices and identify and resolve performance issues.
Configuration Data: Configuration data from network devices such as routers and switches help administrators ensure that network devices are properly configured for optimal performance and security.
Event Logs: Event logs from network devices, such as syslog messages, provide information about events and activities on network devices, such as configuration changes, security incidents, and system errors. Event logs help administrators troubleshoot issues, monitor network activity, and detect security threats.
Security Data: Firewall logs and intrusion detection/prevention system (IDS/IPS) alerts help administrators monitor network security, detect and respond to threats, and ensure that security policies are enforced.
User Activity Data: User login/logout events and application usage help administrators monitor user behavior, track user activity, and detect unauthorized access attempts.
Application Performance Data: Some network monitoring solutions can collect data on application performance, such as response times, transaction times, and error rates. This data helps administrators monitor the performance of critical applications and identify and resolve issues that may impact application performance.
Virtualized Environment Data: Data from virtualized environments, such as hypervisors and virtual machines, helps administrators monitor the performance and health of virtualized resources and ensure they’re operating efficiently.
Cloud Services Data: Data from cloud service providers, such as performance metrics, usage data, and security logs, help administrators monitor the performance, efficiency, and security of cloud services.
Quality of Service (QoS) Data: Network monitoring solutions may collect data on Quality of Service (QoS) metrics, such as latency, jitter, and packet loss, to ensure that QoS requirements are being met.
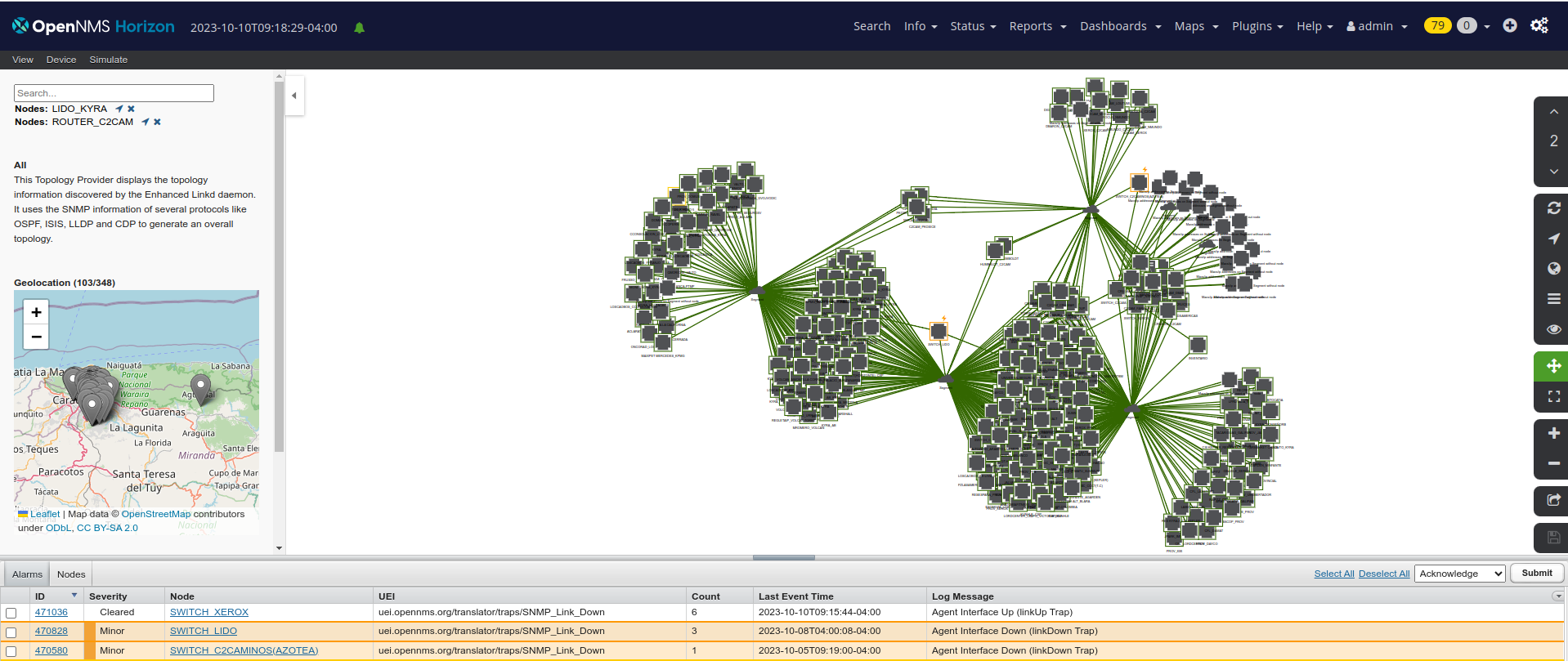
Network Topology Data: Network monitoring solutions may collect data on network topology, including the physical layout of network devices and the connections between devices. This data helps administrators visualize the network layout, identify future bottlenecks or single points of failure, and optimize network performance.
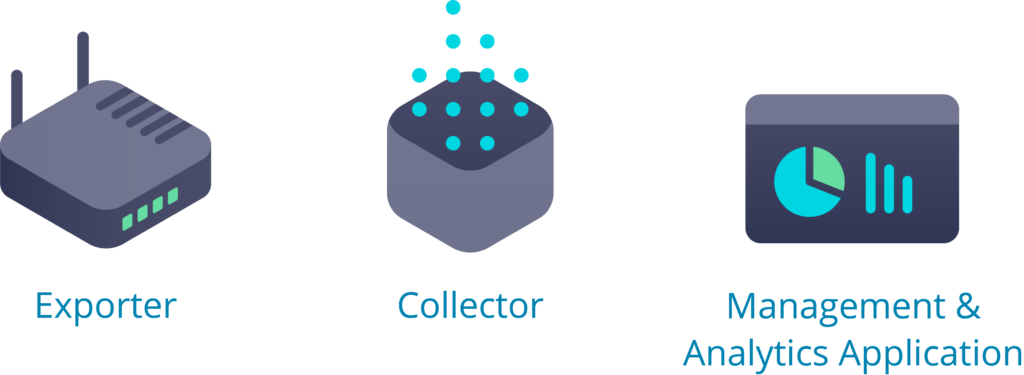
Components of Network Monitoring Solutions
Network monitoring solutions typically consist of several key components that work together to enable network admins to monitor and manage their networks. The exact components may be different depending on the solution and its capabilities as well as the specific needs of the organization, but some common components include:
Data Collection Agents: These agents are installed on network devices to collect data such as performance metrics, traffic data, and event logs. Agents may be software-based or hardware-based, depending on the device and the monitoring solution.
Data Collection and Storage: Network monitoring solutions collect and store data from data collection agents. This data includes performance metrics, traffic data, event logs, and other relevant information. The data is typically stored in a database or data repository for analysis and reporting.
Data Analysis and Processing: Network monitoring solutions analyze and process the collected data to generate reports, alerts, and visualizations. This may involve applying algorithms and statistical analysis to the data to identify patterns, anomalies, and trends.
Alerting and Notification: Network monitoring solutions provide alerting and notification capabilities to alert administrators of critical events or issues. Alerts can notify administrators via email, SMS, or other means when predefined thresholds are exceeded, or anomalies are detected.
Reporting and Visualization: Network monitoring solutions provide reporting and visualization tools to help administrators understand network performance and status. Reports may include summaries of network performance, trends over time, and details of specific events or issues.
Configuration Management: Some network monitoring solutions include configuration management capabilities to manage the configuration of network devices. This may include backing up and restoring configurations, applying configuration changes, and auditing configurations for compliance with best practices and security policies.
Integration and APIs: Network monitoring solutions may offer integration with other systems and tools through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). This allows administrators to integrate network monitoring data with other systems, such as ticketing systems, logging systems, and automation tools.

Best Practices for Implementing Network Monitoring Programs
Regardless of the solution you choose, implementing a network monitoring solution consistently requires strategy, planning, measuring results. These best practices are a good place to start.
Define Clear Monitoring Objectives: Determine what aspects of the network you need to monitor (e.g., performance, availability, security) and what specific metrics are most relevant to your organization's goals.
Regularly Review and Update Monitoring Configurations: Network monitoring is not a set-it-and-forget-it task. Regularly review and update your monitoring configurations to ensure they align with your organization's changing needs and priorities. This includes adding new devices to be monitored, updating monitoring thresholds, and adjusting alerting settings.
Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Focus on monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) that are most relevant to your organization's goals. This might include network uptime, response times, and bandwidth utilization. Monitoring KPIs can help you identify trends and make informed decisions about network optimization and resource allocation.
Implement Comprehensive Security Monitoring: Network monitoring solutions should include robust security monitoring capabilities to detect and respond to security threats. This includes monitoring for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts and malware infections, and implementing measures to protect against these threats.
Train Staff on How to Use the Monitoring Solution Effectively: Provide training to staff on how to use the network monitoring solution effectively. This includes understanding how to interpret monitoring data, how to respond to alerts, and how to use the solution's features to troubleshoot network issues.
Integrate Monitoring Data with Other Systems: Network monitoring data can provide valuable insights when integrated with other systems, such as ticketing systems, logging systems, and automation tools. This integration can streamline network management processes and help ensure a coordinated response to network issues.
Review and Improve Monitoring Processes: This might include adding new monitoring checks, refining alerting thresholds, or implementing new monitoring tools or techniques.
Network Monitoring for Highly Distributed Networks
As your enterprise network edge expands with more devices, processes, services, and physical locations, so does the challenge of monitoring that distributed environment.
Security, privacy, reachability, and latency issues are more prevalent in highly distributed networks. This makes monitoring, collecting, and processing large volumes of data increasingly difficult.
Reaching and monitoring infrastructure, services, and applications located in remote sites within large, distributed networks can be challenging from a central location, such as a data center or the cloud. Specific roadblocks include firewalls, network address translation (NAT) traversal, overlapping IP address ranges, and locked-down environments.
A distributed environment requires an even more sophisticated and advanced network monitoring solution. It must be deployable in a dispersed configuration to reach into systems and networks that would otherwise be inaccessible while keeping the monitoring logic centralized for easier operation and administration.
To adapt to these changing environmental demands and ensure maximum uptime and optimal performance of your network, distributed network monitoring solutions should deliver:
- Distributed data collection: Monitor all systems and networks, including remote and restricted locations beyond the traditional reach of centralized monitoring solutions.
- Digital experience monitoring (DEM): Get different perspectives to better understand local user conditions.
- Dynamic scaling: Adapt to changing network conditions and volumes of data collected for processing and storage.
- Extended network access: Monitor devices with many different APIs or agents across the public internet without compromising security.
- Centralized data visualization, storage, and alarm correlation: View data from a central location with one tool. Store data for analysis to predict and adapt. Understand your data and improve your team’s responsiveness. Delegate issues to the right people at the right time.
- Customization: Build to your unique monitoring, workflow, and personnel needs.
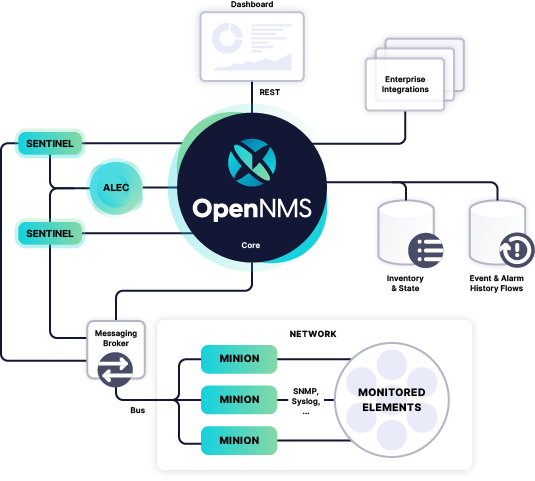
OpenNMS Meridian Network Monitoring
OpenNMS Meridian provides a comprehensive enterprise network monitoring solution that empowers you to ensure the availability and performance of critical network services. It’s a highly scalable open-source network monitoring solution to address all your distributed network challenges:
- It leverages the OpenNMS Minion, a stateless service that communicates with devices and services in remote locations to collect network and device data.
- With perspective monitoring, you can easily monitor the digital experience of internal services and applications from the perspective of many different physical, geographical, or logical locations.
- In scenarios where a high volume of streaming data needs processing, OpenNMS can scale different components individually, including Minions, Kafka, Sentinel, Elasticsearch, and Time Series Databases like Cassandra and Cortex.
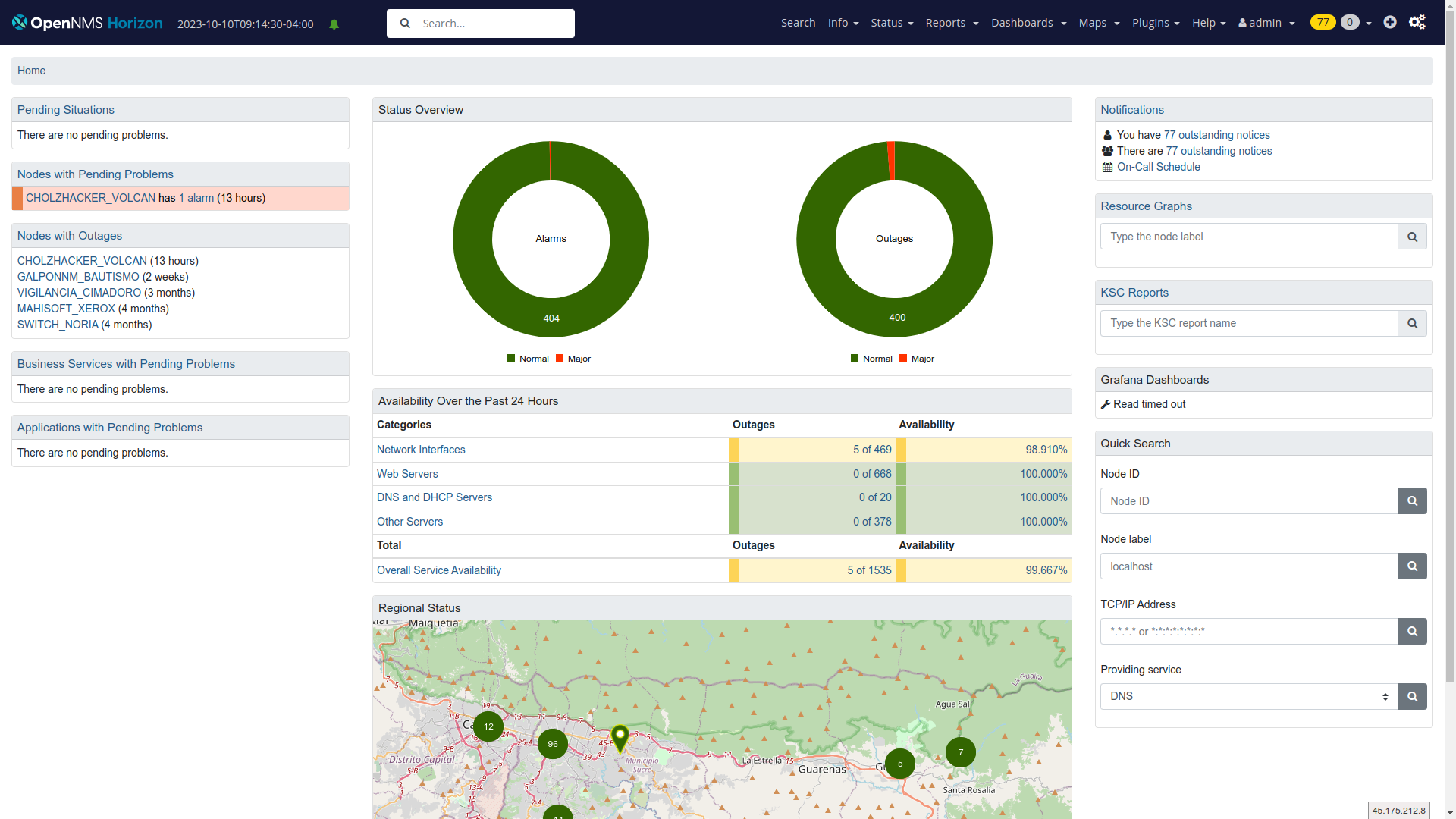
- Built-in Dashboards let you visualize collected data at a glance and provide a common location to view this information. Default graphs for alarms, notifications, outages, and other predetermined insights.
- OpenNMS Meridian provides the ability to correlate related alarms into a single “situation,” making it easier to triage and address underlying problems, reducing the amount of troubleshooting required, and improving response time.
- Finally, OpenNMS allows flexible workflow integration with existing monitoring and management stacks. OpenNMS components and plugins, including Minions, Sentinel, and OpenNMS Plugin for Grafana, are configurable to suit your needs.